News • Genotype-specific strategy
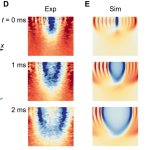
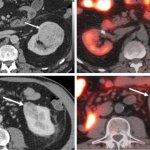
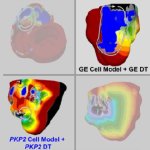
‘Digital twins’ of patients’ hearts give insights into cardiac health
Scientists have developed a tool to create a digital replica of an individual's heart, which could inform the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases.