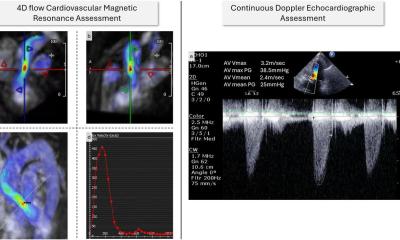
Image source: Garg et al., European heart Journal 2022 (CC BY 4.0)
News • Cardio-imaging
MRI could revolutionise heart failure diagnosis
Until now, the best way of diagnosing heart failure has been an invasive assessment, but it carries risks for patients. Non-invasive echocardiogram, which is based on ultrasound, are usually used instead, but they are wrong in up to 50 per cent of cases.
A new study published in the European Heart Journal shows how magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is superior to Echocardiography for diagnosing heart failure, as well as being a powerful tool to predict patient outcomes, including death. Lead researcher Dr Pankaj Garg, from University of East Anglia (UEA)’s Norwich Medical School, said: “Heart failure is a dreadful condition resulting from rising pressures inside the heart. The best method to diagnose heart failure is by invasive assessment, which is not preferred as it has risks. An echocardiogram, which is an ultrasound of the heart, is usually used to predict the pressure in the heart. However, it is not very accurate. We wanted to find out if MRI scans might offer a better alternative.”
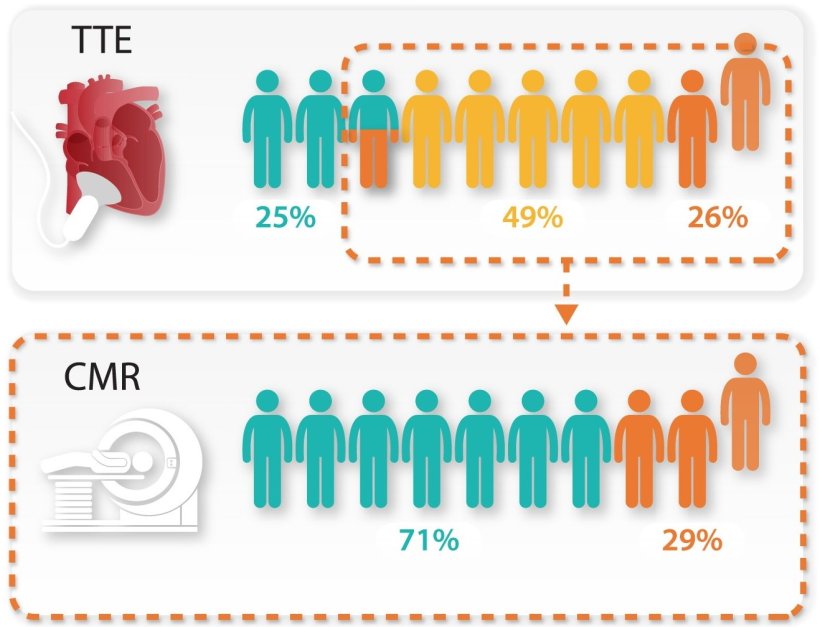
Almost 71 per cent of patients who had wrongly measured pressures by Echocardiography had correct pressures by heart MRI. These findings will reduce the need for invasive assessment
Pankaj Garg
The research team studied 835 patients who received an invasive assessment and a heart MRI on the same day from the ASPIRE registry - a database of patients assessed at the Sheffield Pulmonary Vascular Disease Unit. Dr Garg said: “We investigated if heart MRI can predict invasively measured left ventricular filling pressure. Once we had identified the key parameters - left atrial volume and left ventricular mass - we created an equation to non-invasively derive the pressure in the heart. This simple equation can be applied in any centre around the world which does heart MRI. We also tested the equation in a separate group of patients and demonstrated its reliability. We showed that heart MRI is superior to Echocardiography in predicting pressure inside the heart. Almost 71 per cent of patients who had wrongly measured pressures by Echocardiography had correct pressures by heart MRI. These findings will reduce the need for invasive assessment. This is not only cost-effective but also reduces risks to patients, as a heart MRI scan is a completely non-invasive test. We also showed that the results from heart MRIs were powerful tools to predict whether a patient would live or die. This research was not possible without technical expertise at Norwich and Sheffield and also the rich haemodynamic data from the ASPIRE registry.”
The study was funded by research grants from the Wellcome Trust and the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR), the research partner of the NHS, public health and social care. Senior author Dr Andy Swift, the from University of Sheffield and a Consultant Radiologist, said: “This simple diagnostic equation is very clinically useful and will help doctors predict the pressure in the heart and diagnose heart failure. Testing the use of the equation at other hospitals is the next step to assess the benefit to patients and the reduced need for invasive tests.”
Source: University of East Anglia
06.05.2022