News • Thermogenesis
How Alzheimer's (quite literally) fries the brain
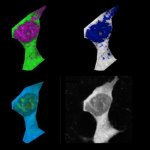
Researchers have shown that aggregation of amyloid-beta, one of two key proteins implicated in Alzheimer’s disease, causes cells to overheat and ‘fry like eggs.’

Researchers have shown that aggregation of amyloid-beta, one of two key proteins implicated in Alzheimer’s disease, causes cells to overheat and ‘fry like eggs.’
A simple blood test could be a better predictor of whether cancer immunotherapy will be successful for a patient with lung cancer than an invasive tumor biopsy procedure.
Over the last 50 years, malaria parasites have developed resistance to seven drugs, but a new way to identify future antimalarials holds promise.

Researchers have developed 3D printed artificial heart valves designed to allow a patient’s own cells to form new tissue.
Newly engineered in vitro tumour models open ways to better understand the crosstalk between liver cancer cells and their microenvironment, researchers from Singapore found.

Latest developments in computational protein design enable the simulation of sequence and structural changes in proteins for creating novel agents in human medicine.

When a virus makes its way into the body, one of the immune system’s first responders is a set of pathogen-removal cells called macrophages. But they don’t all target viruses in the same way.
Hospital-acquired infections are dangerous for patients and costly for clinics. A novel surface treatment could help improve the safety of medical devices and ease the economic burden.

Glucose is absorbed from the foods we eat and fuels every cell in our bodies. But could it also power tomorrow’s medical implants? According to a team of engineers, it might.
In patients with serious and long-term Covid-19, disturbed blood coagulation is often observed. Now, Swedish researchers found a connection between harmful amyloid production and Covid-19 symptoms.
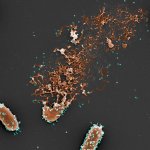
Bacteriophages – viruses that kill bacteria – could be a solution for fighting antibiotic-resistant pathogens, French researchers have developed a model to better predict their efficacy.

A research team in Spain and the US has created 3D-printed acoustic holograms to improve the treatment of diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, among others.
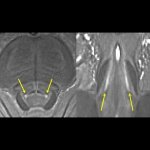
Ultra-powerful 7T MRI scanners could be used to help identify patients with Parkinson’s disease and similar conditions who are most likely to benefit from new treatments, say scientists.

The path from evidence-based research to clinical implementation is straightforward in theory but taxing in practice: Research groups must be coordinated, relevant published material identified, classified, and prepared, to shape findings into a comprehensive SOP for clinical use. To facilitate this complex process, Wolters Kluwer developed a new suite of applications, called Ovid Synthesis.
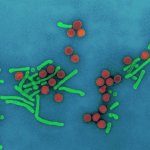
Scientists from France and Belgium gained insights into the structure and function of a central liver protein: NTCP, a cellular-entry pathway for bile salts – but also for certain hepatitis viruses.
Swiss researchers discovered how different cell types in cortex change their activity during general anesthesia, helping to understand how unconsciousness may be induced.
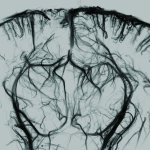
Two successive studies highlight advances in non-invasive 3D ultrasound imaging, making it possible to observe blood flow in real time in the heart and the brain.
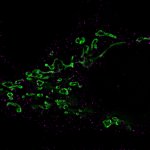
Dormant herpesviruses induce their reactivation via a previously unknown cellular mechanism mediated by a viral microRNA, Würzburg researchers discovered.
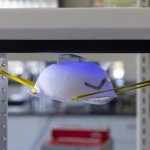
UV radiation is one of the go-to methods for preventing the spread of SARS-CoV-2. But what UV dosage kills the virus? What wavelength? How long? A new study answers many of those questions.
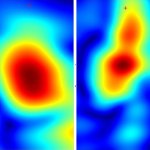
A new handheld device has been developed to painlessly identify skin cancers using millimeter-wave imaging. This could slash the rate of unnecessary biopsies.

In an online event to mark International Women’s Day, five women at various stages of their careers in cancer care discussed the hurdles they had to overcome – often because of their gender – and their determination to succeed.
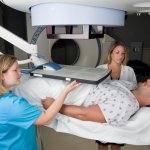
A different way of treating people with prostate cancer will be investigated by researchers at the University of Leeds in a new clinical trial funded by Yorkshire Cancer Research.

A team of researchers from Singapore has developed a novel magnetic therapy that serves as an effective companion therapy to chemotherapy to enhance treatment outcome for breast cancer.

A method for delivering genetic material to the body that has proven useful in Covid-19 vaccination is now being tested as a way to repair damaged heart muscle after a heart attack.

Scientists have taken the first step to creating the next generation of wearable health monitors, which could monitor the body’s health by detecting the gases released from a person’s skin.