News • Skin cancer research
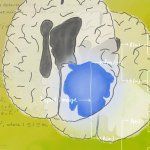
Aggressive melanoma: cells at tumour's edge are key to cancer spread
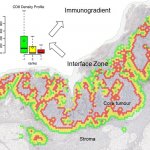
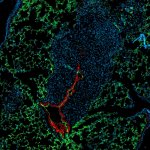
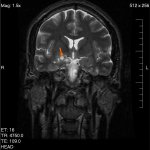
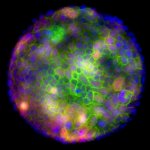
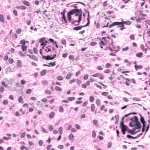
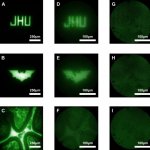
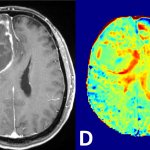
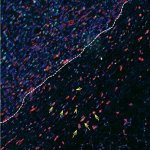
Research led by Barts Cancer Institute (BCI), Queen Mary University of London, has revealed novel insights into the mechanisms employed by melanoma cells to form tumours at secondary sites around the body. The findings from the study may help to identify new targets to inhibit melanoma spread and guide treatment decisions in the clinic.