News • Contamination during procedure suspected
Microplastics found in patients after heart surgery
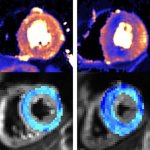
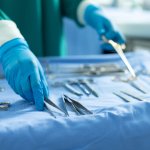
In a pilot study of people who underwent heart surgery, researchers report that they have found microplastics in heart tissues, suggesting they were unexpectedly introduced during the procedures.