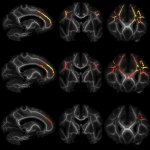
News • Diffusion-tensor and correlated diffusion imaging
New MRI technique captures Covid-19’s impact on the brain
An MRI invention from engineers at the University of Waterloo reveals better than many existing imaging technologies how Covid-19 can change the human brain.