Article • Expert perspectives from ESC 2025
Faster, smarter, deeper: how new technologies redefine cardiac imaging
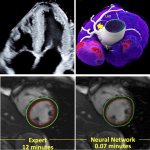
Cardiac imaging is evolving, and new techniques continue to uncover the secrets of the heart for cardiologists who know how to use them. At the ESC 2025 Congress in Madrid, four experts explored cutting-edge developments across different modalities. Ranging from AI-assisted ultrasound image acquisition and accelerated MRI protocols to advanced prognostic tools for CT and nuclear imaging, these…