News • 3D-printable polymer
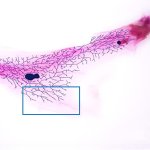
Print, stretch, implant: new material could help build artificial organs
Researchers have developed a novel 3D-printable material that is both biocompatible and highly elastic. The technology could pave the way for artificial organs and improved drug delivery systems.