
News • Ocular sensor
Researchers develop contact lenses to diagnose glaucoma
A team from the UK and Turkey have developed a contact lens with embedded micro-sensors which can detect changes in eye pressure - a possible indicator of glaucoma.

A team from the UK and Turkey have developed a contact lens with embedded micro-sensors which can detect changes in eye pressure - a possible indicator of glaucoma.
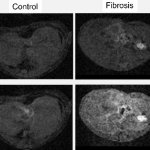
A research team has developed a nanoparticle-based contrast agent with the properties necessary to successfully use MRI for targeted diagnosis of liver fibrosis.
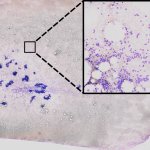
Certain genetic features are crucial for treatment decisions for AML leukaemia. A team from Münster shows how an AI-based method can predict these features from images of bone marrow smears.

Clinicians tend to disregard patient self-assessments for their diagnostic decisions, new research suggests – a mistake that might cause those patients unnecessary harm.

While genetic information may lead to better treatments, promises of cost savings are unfounded. Instead, a large additional bill is more likely, according to University of Copenhagen researchers.

A new approach to the identification of harmful bacteria: A new study explores how spectroscopic techniques can be used for quick analysis directly from the skin.
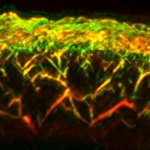
Using AI and optoacoustic imaging, researchers have developed a new method to assess microvascular changes in the skin – and thus the severity of diabetes in the patient.
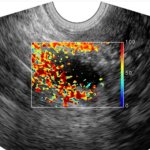
Researchers and clinicians at Washington University in St. Louis found a way to improve diagnostic accuracy of potentially cancerous lesions in the ovaries and adnexal regions, or the fallopian tubes.

Researchers from the University of Birmingham have designed and developed a novel diagnostic device to detect traumatic brain injury (TBI) by shining a safe laser into the eye.
Researchers have developed a method for assessing the number and structure of aggregated blood platelets (or thrombocytes) that can potentially help quantify the risk of a severe Covid-19 infection. As a result, they have identified a predictive biomarker for the seriousness of a Covid-19 infection. This will allow physicians to adjust treatment at an early stage. The researchers used a method…

Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, a non-profit hospital and medical research institution in Los Angeles, is setting new standards for quality and innovation in patient care by successfully introducing typing of Candida auris species – a procedure that could prove crucial in protecting patients from infection outbreaks caused by these microbes in healthcare settings.
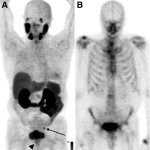
Bone scans have been found to overstage prostate cancer at initial staging compared to prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) PET, according to new research.
Faster, more accurate and cost-effective testing: Experts outline the beginnings and evolution of “lab-on-a-chip” technology, and its benefits for advanced and next-gen operational platforms.
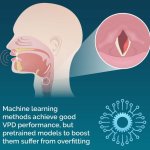
Voice pathology detection (VPD) can detect abnormal vibrations in the vocal cords caused by conditions like cancer and cysts. Now, researchers have found a way to make the method more reliable.

A team at the University of Bristol has developed a robot manipulator that could carry out clinical breast examinations. The developers hope the device will revolutionise breast health monitoring.

New research from Deusto University in Bilbao, Spain, provides evidence that people can inherit artificial intelligence biases (systematic errors in AI outputs) in their decisions.
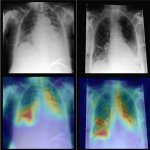
A new artificial intelligence (AI) model combines imaging information with clinical patient data to improve diagnostic performance on chest X-rays, a new study finds.
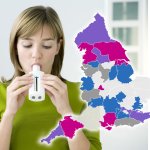
A new survey by The BMJ reveals shortages of vital diagnostic tests for respiratory conditions, such as COPD and asthma, across some of the most deprived areas of England.
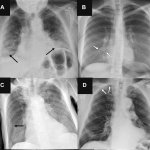
Reports of AI gaining the upper hand in diagnostic imaging interpretation are piling up, but there are still areas where the eye of a trained human radiologist remains superior.
Could a single biomarker detect all types of diseases related to dopamine deficiency in the brain? According to a Swedish research group, such a marker may have just been found.
Two out of the four screening tools used by emergency medical services are inadequate for recognising sepsis, according to new research presented at the EUSEM Congress.

A new device that combines microfluidics on paper, electrochemical transduction and immunoassays on magnetic nanoparticles is useful for easy and rapid diagnosis of lung diseases.

Combining ultrasound and MRI technology can help detect prostate cancer at an earlier stage and potentially save lives, according to new University of Dundee research.
Researchers at Monash University have designed a new co-training AI algorithm for medical imaging that can effectively mimic the process of seeking a second opinion.

With the introduction of digital pathology, the University of Queensland and Sullivan Nicolaides Pathology aim to provide significantly improved tests in terms of cost, quality and speed.