
News • Comparison of imaging methods
4D flow MRI to quicker diagnose aortic stenosis
A new 4D flow MRI method could accelerate diagnosis of aortic stenosis, a progressive and potentially fatal heart condition.

A new 4D flow MRI method could accelerate diagnosis of aortic stenosis, a progressive and potentially fatal heart condition.

Multiple sclerosis often transitions from a relapsing-remitting to secondary progressive form, which requires different treatment. Now, an AI model can determine this change with 90% certainty.

Pupil dilation and involuntary facial movements could provide a window into diagnosing tinnitus. A new method uses AI to detect minuscule reactions to various sounds and noises.

During the Covid-19 pandemic, everyone became familiar with lateral flow tests. These tests generate a lot of plastic waste, creating an environmental crisis. Experts call for urgent action.
Pancreatic cysts (IPMNs) are seen as a precursor of pancreatic cancer. However, not all patients need to undergo surgery. A recent study may help patients with IPMNs to avoid unnecessary surgery.

Nuclear medicine (NM), one of the more mature technologies of diagnostic imaging, has been experiencing a rebirth in innovation and interest. The increasing prevalence of cancer,, an aging global population, and greater longevity, has created a robust demand for nuclear medicine. At ECR in Vienna, presenters explored market perspectives, but also safety and sustainability challenges.

While generative AI shows immense potential for healthcare, a critical reliability issue lurks beneath the surface: LLMs don't think like doctors do, a data science expert explained at the Emerging Technologies in Medicine (ETIM) congress in Essen. This potentially fatal flaw, however, may be fixable, he suggested.
Despite previous global declines, pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) is on the rise again. A new AI-powered lung ultrasound shows promise in improving diagnostic performance of TB.

A new study found that a significant proportion of Parkinson's disease diagnoses are later corrected. The results demonstrate the need for improved diagnostic processes.
A new device for people with or without medical training could be used as an easier, more forgiving alternative to stethoscopes to accurately detect valvular heart disease (VHD).

A new method to quickly and accurately analyze the structure of collagen in tissue shows promise to improve the diagnostics of cancer and other diseases.

To diagnose prostate cancer, an MRI-guided biopsy is often performed. Now, a study shows that micro-ultrasound is just as effective, cheaper and easier to use. This could help free up MRI capacities.

A new rapid diagnostic test can identify pregnant women at elevated risk of transmitting hepatitis B to their babies. This could help prevent mother-to-child transmission during childbirth.
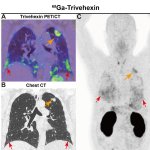
Nuclear medicine specialists have successfully used the radiopharmaceutical Ga-68-Trivehexin from Trimt to accurately diagnose patients with pulmonary fibrosis and concurrent lung cancer.

A newly-developed robot can detect medication side-effects in patients after heart arrhythmia treatment faster than a human doctor, while reducing the number of follow-up tests.
MRC Holland recently announced that five SALSA MLPA assays for the detection of hereditary breast and ovarian cancer (HBOC) syndrome were recently CE-marked for in vitro diagnostic (IVD) use under the new In-Vitro Diagnostic Regulation EU 2017/746 (IVDR).

Molecular changes associated with brain inflammation and dementia can be detected in the blood. Researchers want to use this to establish blood tests as an alternative to more costly brain scans.
The Diagnostica e Terapia Centro Aktis in Marano di Napoli, Italy, has expanded its diagnostic department with the addition of three imaging systems from United Imaging.

A new study has shown that the molecular signature of long Covid can be found in blood samples of children. Using an AI tool, the researchers were capable of diagnosing the condition with 93% accuracy.
The installation of a state-of-the-art digital PET/CT scanner in Essen marks the German debut for the technology of United Imaging. The device is designed to deliver precision diagnostics at the Kliniken Essen-Mitte Evang and the private nuclear medicine clinic Nukmed, a premier cancer care institution.
When is a biopsy needed to diagnose a kidney disease? This is handled very differently around the world, a new study finds. This could result in adverse patient outcomes, the researchers warn.

Liverpool physicists have developed a “diagnostic infrared wand” to more accurately predict the prognosis of oral cancer lesions than current H&E staining techniques.
Paediatric brain tumours are difficult to diagnose and treat – especially, when delays occur. A new study explored the impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on children with brain tumours.
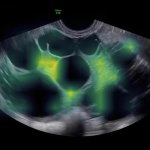
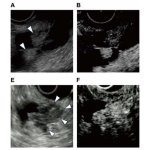
Ovarian cancer is common and often only detected by chance. A newly developed AI-based model could help differentiate between benign and malignant ovarian lesions.

Complex diseases could require complex biomarkers for accurate diagnosis in the years ahead, according to a leading pathologist. In a keynote address to the 36th European Congress of Pathology in Florence, Italy, Professor Manuel Salto-Tellez highlighted this as one of the major future challenges for the discipline. However, he also believes pathologists will sit at the core of modern medicine.