News • Microsatellite instability
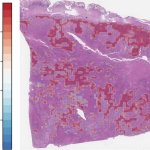
Predicting tumor MSI status for precision cancer treatments
Microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) tumors are associated with better clinical outcomes. A novel AI model for accurate MSI prediction could help battle gastric and colorectal cancers.