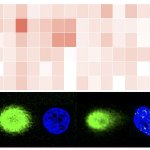
News • New insights on aneuploid epithelial cells
Breast cancer-like cells also found in healthy women
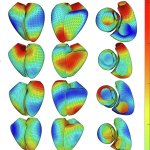
A certain type of cells, called aneuploid epithelial cells, are usually associated with breast cancer. However, new research reveals that they can also be found in healthy women.