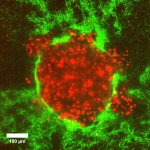
News • Identifying antimicrobials
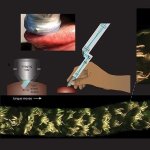
Automated CAST-R system helps to fight blood infections
When treating acute infections, health care providers must quickly identify the best antibiotics for fighting the infection. An automated system provides swift, accurate results for determining the best antibiotics at the right dose.