News • Genetic dystrophy repair
Using mRNA to improve muscle strength
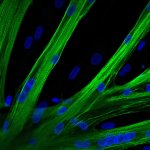
An ECRC research team has introduced CRISPR-Cas9 into human muscle stem cells for the first time using mRNA, thus discovering a method suitable for therapeutic applications.

An ECRC research team has introduced CRISPR-Cas9 into human muscle stem cells for the first time using mRNA, thus discovering a method suitable for therapeutic applications.
A way to replicate what happens inside the heart after cardiac arrest could open new avenues for the study of heart regeneration whilst reducing the use of live animals in research.

Bioengineers have shown they can eradicate advanced-stage ovarian and colorectal cancer in mice in as little as six days with a treatment that could be ready for human clinical trials later this year.

An international team of scientists have shown that small and large bacterial populations follow qualitatively different evolutionary paths to develop antibiotic resistance.
A new study has analyzed over 3000 proteins to identify which are causally linked to the development of severe Covid-19. This provides insight into potential new targets for treatment and prevention.

Scientists have developed a prototype sensor that could help rapidly measure adenosine triphosphate and lactate levels in blood samples, aiding in the rapid assessment of disease severity.

A new study offers hope against liver cancer: A vaccine proved to be safe and effective protection in premalignant and malignant liver diseases in preclinical mouse models.

The Covid pandemic might be responsible for a “substantial decrease” in mental wellbeing in the UK, according to new research from the University of East Anglia and University of York.
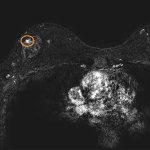
Annual MRI screenings starting at ages 30-35 may reduce breast-cancer mortality by more than 50% among women who carry certain genetic changes in three genes, according to a new modeling analysis.
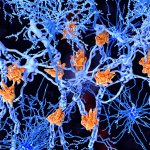
Nerve damage in multiple sclerosis can be detected via the concentration of neurofilament light chain in the blood. This could offer valuable information on future disease course and therapy effectiveness.
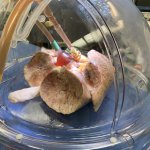
A new study has proved that it is possible to convert blood type safely in donor organs intended for transplantation. This is an important step towards creating universal type O organs.
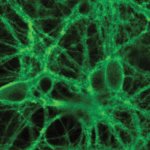
Researchers in Zurich have developed a fluorescent orexin biosensor to observe on of the brain's signaling molecules "live" to gain insights into constant daytime sleepiness (narcolepsy).

Is the Underground a safe means of transport in times of Covid-19? A computer simulation, developed at the University of Leeds, has calculated the infection risk.
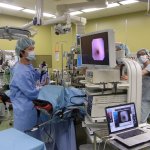
A large-scale study has found that simulation-based surgical training produced an increase of surgeons’ skills for more complex surgeries.
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) develop a protocol to transplant 3D cellular structures that could regenerate damaged intestine.
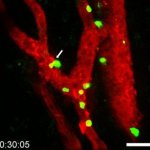
French researchers have found a way to facilitate access to tumours for killer lymphocytes, paving the way for more efficient immunotherapies against cancer.

Engineers at MIT have developed a kind of surgical duct tape — a strong, flexible, and biocompatible sticky patch that can be applied to biological tissues and organs to help seal tears and wounds.
Scientists have investigated the effectiveness of various common hand disinfectants against hepatitis E. They were able to show that most formulations do not completely inactivate the virus.

RNA has already been making an impact in the context of the vaccine program, but the potential of RNA-based compounds is far from being fully tapped, as RNA allows for entirely new therapeutic approaches.
Faulty versions of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are well known to increase the risk of breast and ovarian cancer. Now, they have been linked to several other cancers, including those that affect men.
Professor Richard Neher from the Biozentrum of the University of Basel is using his Nextstrain platform to investigate which variants of the SARS-CoV-2 virus are currently circulating worldwide.

Researchers from Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin and Deutsches Zentrum für Neurodegenerative Erkrankungen (DZNE) present new findings on the immune response against SARS-CoV-2.
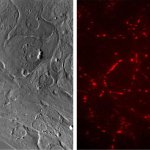
Heart cells from a patient with an inherited heart disease called arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy do not contract correctly when grown in the laboratory, researchers from Osaka University have found.
A new study shows that the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant is less effective than Delta at blocking a cellular defence mechanism against viruses, the so-called 'interferon response'.
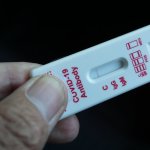
How long can Covid-19 antigen tests reliably tell the antibody status? Researchers at the Paul-Ehrlich-Institut identified several factors that affect the detection duration.