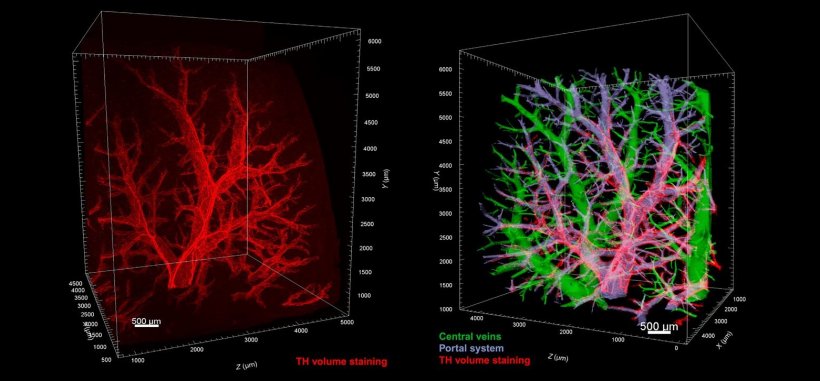
Image source: Adori et al., Science Advances 2021 (CC BY-NC 4.0)
News • NAFLD research
3D imaging reveals neural ‘vicious cycle’ in fatty liver disease
With the application of a novel 3D imaging technology, researchers at Karolinska Institutet have discovered that one portion of the autonomic nervous system in the liver undergoes severe degeneration in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
The study, which is conducted in mice and human liver tissue, shows that the degeneration of nerves is correlated with the severity of liver pathology. The results are being published in the journal Science Advances.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common hepatic disorder, with prevalence around 25 percent globally. Approximately one third of all fatty liver cases will develop to steatohepatitis, which is a severe disease seriously affecting the entire metabolism. In the current paper, researchers explore the nervous system in fatty liver using volume immuno-imaging and light sheet microscopy ― a novel imaging technique, which altogether offer large-scale 3D visualization with cellular resolution. According to the study, this technology can reveal even early, minor or hidden structural impairments of the liver.

Image source: Karolinska Institutet
“Now we know that nerves in the liver have multiple subtle regulatory roles” says Csaba Adori, researcher at the Department of Neuroscience, who led the study. “Their role, however, may be more essential during the fight-or-flight response or when subjected to metabolic challenges. Degeneration of liver sympathetic nerves and abnormal operation of the remaining nerve fibres in the fatty liver could compromise all these functions, which may contribute to further aggravation of the disease, as part of a vicious cycle.”
According to the study, alterations in the liver innervation occurs already in early stages of fatty liver disease. With progression to the more severe steatohepatitis, these impairments turn to a pronounced degeneration of the nerves. The nerve pathology is also similar in mouse model of fatty liver and in human fatty liver samples. The research team now hopes that the study results will open the door for new therapeutic approaches in the treatment of steatohepatitis and portal hypertension, by targeting the liver sympathetic nervous system.
Source: Karolinska Institutet
22.07.2021