News • Environmental and human health research
PHIC: A French-Japanese cooperation for planetary health
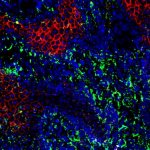
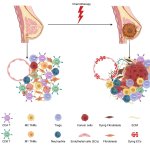
A remarkable collaboration for planetary health: The Institut Pasteur and the University of Tokyo want to establish a joint institution dedicated to addressing human and environmental health research.