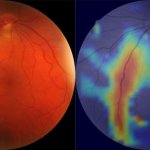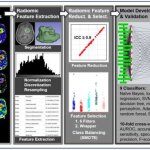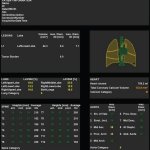
Article • Philips presents portfolio update at ECR 2022
AI-powered MRI to increase imaging speed, reduce staff burden
The portfolio Philips presented at ECR 2022 revealed that the company not only advanced their products, but also listened to medical professionals and patients – and took their feedback to heart.