Image source: Hologic
Sponsored • Breast cancer backlog
Getting cancer screening programmes back on track with AI and digitisation
The Covid-19 pandemic continues to impact people’s health across the world. This goes beyond the disease itself, as healthcare systems adapt how they provide services. Routine screening has been severely affected with screening programmes reduced or paused.
In the short-term, countries are facing a daunting backlog, estimates of which have yet to be fully quantified. In France, the number of breast cancer diagnoses fell 50% from March to May 2020 1 and there are a hypothesised 5,000 undiagnosed cancers in Belgium (between 1 March – 18 September 2020).2 It is critical that screening gets back on track and we believe innovation is a key in both the short and long term.
Breast cancer screening is well suited for digital technologies and the application of artificial intelligence (AI), given it requires highly trained medical professionals to identify rare, subtle changes visually, a process that can be tedious and time-consuming. AI could help to significantly improve this.
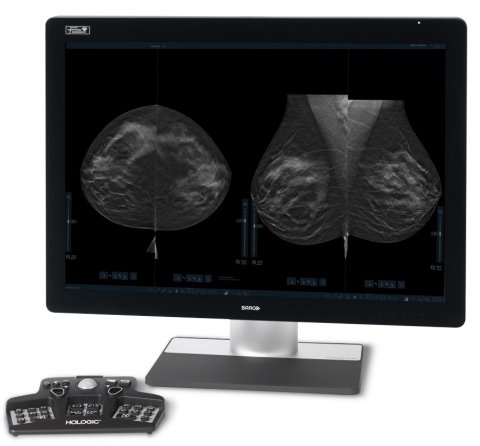
Image source: Hologic
One area where AI-guided imaging can play a role is in workflow prioritisation. Radiologists are facing a growing need for improved workflow efficiency as digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) becomes the gold standard for screening in Europe. The recent European Commission Initiative on Breast Cancer (EBIC) guidelines on breast cancer screening and diagnosis recommend the use of either DBT or digital mammography in screening. However, DBT creates an influx of large file sizes and images that can lengthen the image reading process. This creates a need for solutions like Hologic’s 3DQuorum technology, powered by AI technology, commercially available since October 2020, to help streamline workflow and improve mammography efficiency where possible.
Tomosynthesis, more commonly known as 3D MammographyTM, detects up to 65% more invasive breast cancers, and reduces recalls of patients by up to 40%, when compared to conventional 2D mammography alone.3,4 With Hologic’s 3DQuorum technology which uses AI, the number of 3D images to review is reduced by two-thirds, saving an average of one hour per eight hours of daily image interpretation time.5,6 This time saving could mean that radiologists could read more cases a day and potentially clear the backlog more quickly.
Additionally, AI has the potential to increase breast cancer screening capacity by removing the need for review by two readers. When integrated into a screening programme, it could effectively and efficiently highlight the areas that are of particular interest for the reader.
Another opportunity is applying AI to risk stratification. It could help to identify and prioritise screening for women with a high risk of breast cancer e.g. women with dense breasts. Dense breasts make it more difficult to identify cancerous cells in standard mammograms meaning cancers may be missed or women are recalled for unnecessary further investigation.
Diagnostic innovation is on a trajectory that we cannot ignore; we must harness its power, so breast cancer screening programmes get back on track. AI is a fundamental piece of the innovation puzzle and we are proud to be at the forefront of AI solutions for our customers and partners.
References:
1 MISC-07567-EUR-EN Finsbury International Policy & Regulatory Advisers (2021). Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on breast cancer screening in Italy, France, Spain and UK. Internal FIPRA report. Unpublished.
2 Belgian Cancer Register [Internet]. COVID-19. 2020 – c2020 [cited 2020 20 Nov]. Available from: https://kankerregister.org/default.aspx?PageId=204 Last accessed May 2021
5 Clinical Report: CSR-00116. Rev 004. Section 4.4. Dimensions Breast Tomo Physician Labeling_3DQuorum - MAN-06153 Rev 002. Section 1.4
6 Clinical report: CSR-00116. Dimensions Breast Tomo Physician Labeling_3DQuorum - MAN-06153 Rev 002. Section 1.10. Supplement User Guide 3DQuorum - MAN-06029 Rev 002. Section 1.4.
15.07.2021