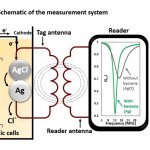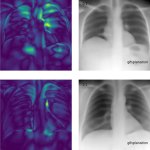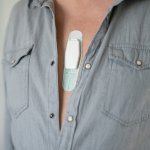
Opinion article • Wearable medical devices
Sweat analysis reveals a wealth of health information
Diagnosis and monitoring medical conditions, including cancer, diabetes, heart disease, and infections: In this opinion article, Alix Joseph (Linxens) explores the potential of sweat analysis.