News • Updating treatments
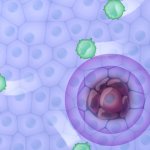
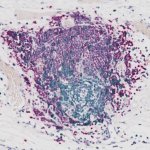
Sugar and fat can make cancer cells harder to kill
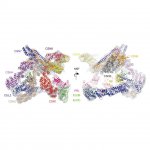
In their quest to find new and better methods to make cancer cells more susceptible to treatment, Karin Lindkvist and her research group at Lund University in Sweden are looking into the world of molecules, using the X-rays at the MAX IV laboratory. The researchers believe that limiting the cells' access to sugar will make cancer cells more sensitive to treatment. Many of the cancer treatments…