Article • Cancer screening
The need for breast imaging for transgender patients
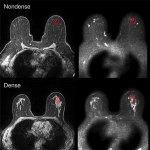
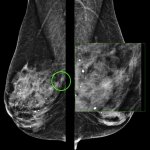
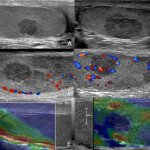
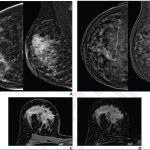
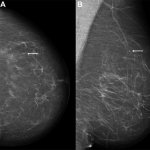
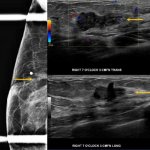
The need for breast cancer screening of transgender individuals has been a topic of uncertainty until recently, due to lack of reliable patient data, consensus by radiologists, published research, and recommended guidelines. A 2021 survey of Society of Breast Imaging (SBI) members revealed that ‘breast radiologists differ in their practice and knowledge regarding screening of transgender…