Article • Phase-contrast x-ray
Creating the Holy Grail of medical imaging
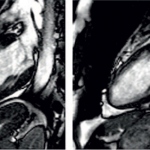
Among new medical imaging innovations is a phase-contrast x-ray technique to bring greater precision to breast cancer assessment and improve biopsy diagnostics. EH asked research pioneer Professor Marco Stampanoni, a key figure in the development of this technique, to explain how it works. Report: Sascha Keutel