News • Chasing the causes of cancer
Mapping cancer-related proteins in unprecedented detail
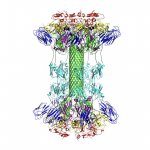
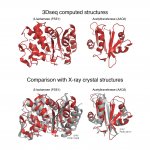
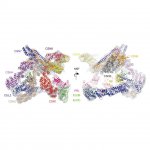
Researchers at the Institute of Cancer Research (ICR) have gained new understandings of two key complexes of cancer-related proteins by producing the most detailed ever maps of the structures they form when they come together. The study reveals that the two protein complexes come together in cells in a series of steps that change how their individual component proteins are arranged together. It…