News • Study shows widespread disruption
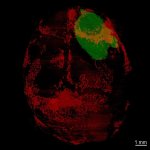
Glioblastoma: damage beyond the brain
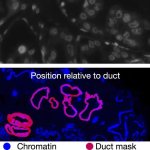
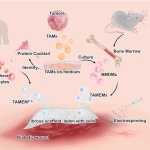
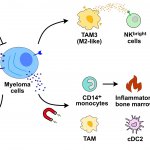
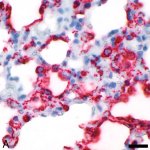
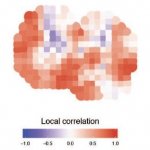
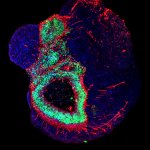
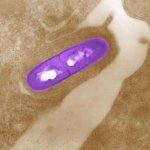
Scientists have shown for the first time that glioblastoma—the deadliest form of brain cancer—affects not just the brain but also erodes the skull, alters the makeup of skull marrow, and interferes with the body’s immune response.