News • Fertility research
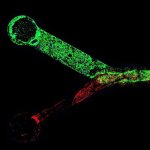
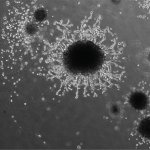
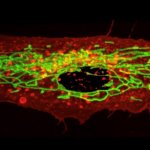
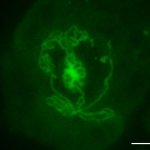
Researchers produce testicle organoids in the lab
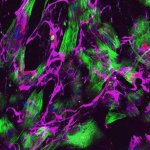
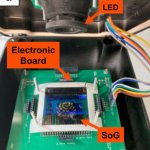
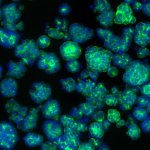
A research team created "laboratory testicles" that may significantly advance understanding of the mechanisms involved in sex determination and provide solutions for male infertility.