News • Image analysis
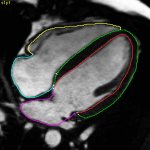
Deep learning model detects prostate cancer on MRI scans
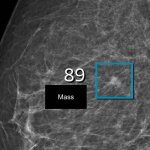
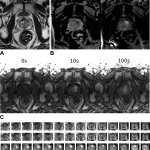
The interpretation of prostate MRI is notoriously difficult. Annotating AI shows promise to help improve diagnostic performance through increased cancer detection rates with fewer false positives.