News • Increasing cell visibility
Making cancer easier to find and destroy for the immune system
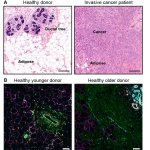
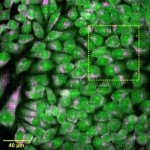
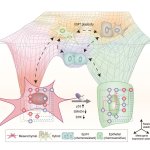
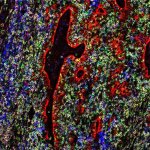
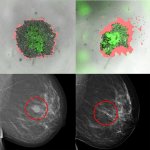
Researchers in Japan and the US have developed technology to robustly augment the amount of MHC class I molecules in cancer cells. This makes them easier to find and destroy for the immune system.