News • Tissue dissection
World‘s first automated high throughput tissector launched
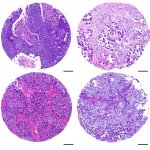
Molecular pathology company Xyall BV launches its Tissector High Throughput (HT) system for precision diagnostics. This is a world first – enabling high volume, molecular diagnostic laboratories to capitalize commercially on the company’s automated tissue dissection technology.