News • Infection control
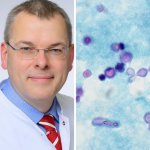
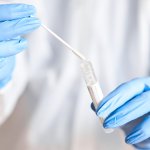
C. diff: diagnostic stewardship reduces unnecessary testing
A new study describes the outcome of a new approach to testing for Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) guided by the principles of diagnostic stewardship, to help rein in the overtreatment of patients.