Sponsored • Accutron CT-D Vision
The next generation of CT contrast media injectors
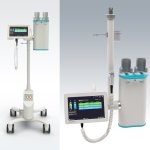
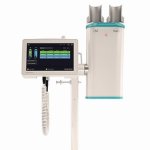
The Accutron CT-D Vision is the next generation of Medtron AG’s leading CT contrast media injector. Focusing on the user’s needs, the latest stage of development of the Accutron CT-D improves the usability of the CT injector and optimizes its integration into the radiological environment.