Image source: RSNA
News • Coronary plaque vulnerability
Using radiomics to predict heart attacks
Researchers are using an approach called radiomics to predict future cardiac events like heart attacks, according to a new study.
The work was published in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). Radiomics allows researchers to extract quantitative, or measurable, data from CT images that can reveal disease characteristics not visible in the images alone. Coronary artery disease is linked with fatty deposits of plaque that build up inside the artery walls. Large, lipid-rich plaques are vulnerable to rupture. The rupture of these plaques causes most heart attacks. However, predicting which plaques will rupture is challenging.
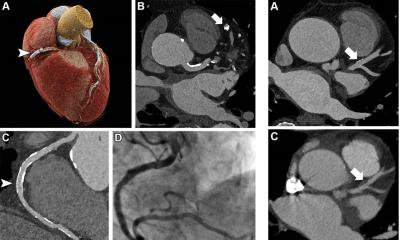
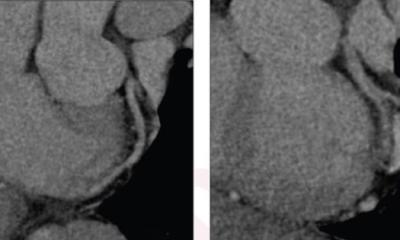
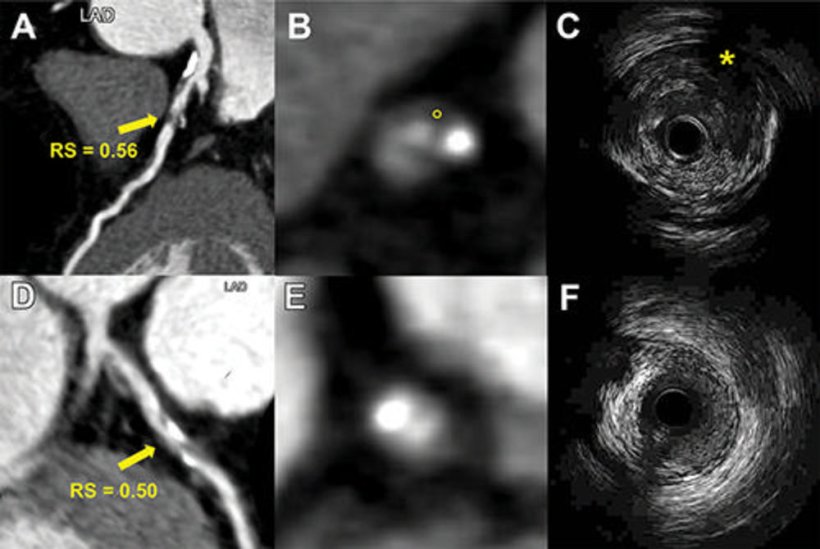
Researchers in China developed a radiomics model that uses information from coronary CT angiography images to assess plaque vulnerability. They developed the model in 299 patients. They then studied the approach in 708 patients with suspected coronary artery disease.

Image source: RSNA
The model enabled the detection of vulnerable plaques associated with an increased risk for major adverse cardiac events like heart attacks. A high radiomic signature was independently associated with these events over a median three-year follow-up. "The results of this study are encouraging and exciting," said study co-lead author Long Jiang Zhang, M.D., Ph.D., from the Department of Radiology at Jinling Hospital, Medical School of Nanjing University in Nanjing, China. "Radiomics provided a more accurate approach to detect vulnerable plaques compared to conventional coronary CT angiography anatomical parameters."
The radiomic signature would be easy to add into clinical practice, Dr. Zhang said. In the clinic, it could assess potentially vulnerable plaques and help stratify high-risk patients. "If the radiomics analysis is embedded into the routine CT angiography workstation, it can automatically identify vulnerable plaques for clinician review," Dr. Zhang said. "Thus, radiomics may significantly improve the accuracy and precision of high-risk plaque detection in routine clinical practice."
The researchers intend to build a radiomics model from different scanner types and vendors. They also are planning a larger, multicenter study of 10,000 patients. "With the support of large observational studies and randomized controlled trials, the radiomics approach may help guide clinical decision-making and improve patient care in the future," Dr. Zhang said.
Source: Radiological Society of North America
16.02.2023