News • MS
How do immune cells enter the cerebrospinal fluid?
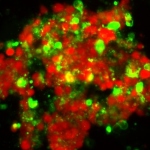
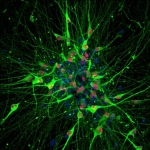
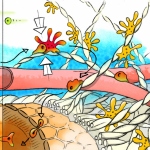
A research team headed by scientists at the Institute of Neuroimmunology and the Institute for Multiple Sclerosis Research (IMSF), University Medical Center Göttingen (UMG), has gained new insights into the immune function of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). They used real-time microscopy to film the lively trafficking of immune cells between the CSF and the nervous tissue. Here the meninges play the…