Deadly dance between nerves and cancer cells
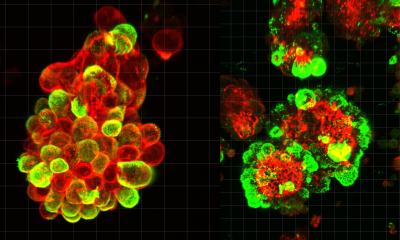
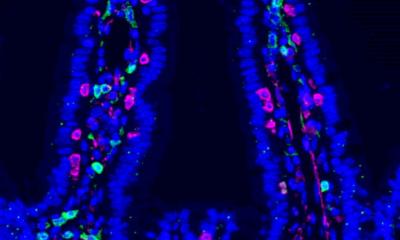
In certain types of cancer, nerves and cancer cells enter an often lethal and intricate waltz where cancer cells and nerves move toward one another and eventually engage in such a way that the cancer cells enter the nerves.
The findings, appearing in Nature Communications, challenge conventional wisdom about perineural invasion, which holds that cancer cells are marauders that invade nerves through the path of least resistance, said Nisha D'Silva, principal investigator and professor at the University of Michigan School of Dentistry.
D'Silva's lab discovered that perineural invasion is actually a much more intricately choreographed biochemical give-and-take between the nerves and the cancer cells. "Once head and neck cancer invades the nerves, it is one of the worst things that can happen," said D'Silva, who also has a joint appointment at the U-M Medical School Department of Pathology and is a member of the U-M Cancer Center's Head and Neck Oncology program. "It is highly correlated with poor patient survival, and there is no targeted treatment for it because it is not known why some tumors do this and some don't."
Perineural invasion is seen most in head and neck, pancreatic, stomach and colon cancers, and causes severe pain or numbness, tumor spread and recurrence, and loss of function, among other complications. D'Silva's lab found that perineural invasion begins when the nerve releases a stimulus that triggers a specific protein receptor in cancer cells. The receptor activates instructions in the cancer and releases the same stimulus back to the nerve.
The nerve recognizes the stimulus, which causes the nerve to 'reach' toward the cancer--imagine two dancers recognizing each other across a room and slowly moving closer until they become permanent partners. After this initial pairing up, the loop continues. "Basically it's like they are waltzing," D'Silva said. "It is a very elegant dance, if you will."
It is extremely difficult to study perineural invasion in head and neck cancer, so D'Silva's lab had to develop a way to observe these interactions in live samples. First, researchers implanted the nerve in chick egg membranes, and after the nerve integrated, they studied the interactions between the nerve and head and neck cancer cells. D'Silva said the next steps in the research are to find out, "when and how we can interrupt the dance."
Source: University of Michigan
29.04.2015