News • Research into fat cells
Healthy adipocytes keep breast cancer at bay
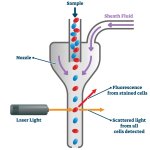
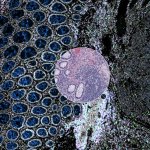
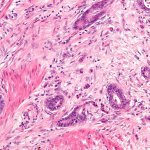
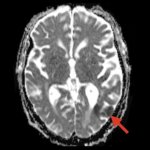
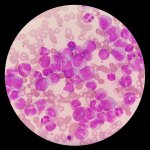
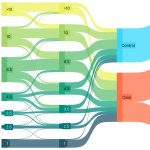
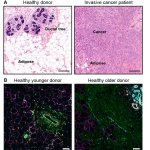
Researchers have found a possible explanation as to why higher breast density and older age increase the risk of breast cancer. According to the experts, adipocytes play a vital role here.