Image source: Andreas Heddergott/TUM
News • Model system shows tumor grwoth
Novel organoid model for pancreatic cancer
Researchers at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) have developed a novel model system that can be used to precisely track the growth steps and three-dimensional arrangement of pancreatic cancer cells. It also provides the basis for testing and developing therapeutic approaches.
The researchers present their findings in the journal Nature Communications.
Pancreatic cancer accounts for around 3 percent of all cancer cases in Germany. Although this type of cancer is relatively rare, it is highly aggressive and therefore lethal in most cases. “There is probably no other tumor type where research is so urgently needed,” says Maximilian Reichert, professor for translational pancreatic carcinoma research at TUM Klinikum rechts der Isar. “In contrast to other tumor types such as breast or colorectal cancer, we neither have meaningful early detection programs nor effective treatments.”
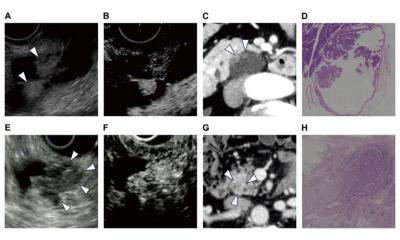
An interdisciplinary research team led by Maximilian Reichert and Andreas Bausch, professor for cellular biophysics at TUM, has therefore developed a tumor organoid derived from the pancreas. “An organoid is a three-dimensional cell culture that recapitulates key features of the tissue of origin – in this case pancreatic cancer,” explains Reichert. Until now, organoid models have always been spherical aggregates of cells. They reflect the molecular characteristics of the tissue, however so far, failed to mirror tissue architecture, which can ultimately be crucial for the function. “We have succeeded for the first time in modeling the morphology of the tumor, consisting of complex tubular structures that are so characteristic of pancreatic cancer,” says Reichert.
It is not only the biochemical conditions, but also the mechanical properties of the matrix that decisively impact growth
Andreas Bausch
For cells to grow as this multi-branched structure outside the body, they not only need the nutrients in which they can thrive. They also must be embedded in a matrix where they can form a structure through cellular division and migration. The TUM researchers used a matrix primarily composed of collagen. “By doing that we changed the mechanical conditions of the matrix in which the cells grow to permit the formation of complex structures,” says Bausch. “It is not only the biochemical conditions, but also the mechanical properties of the matrix that decisively impact growth.”
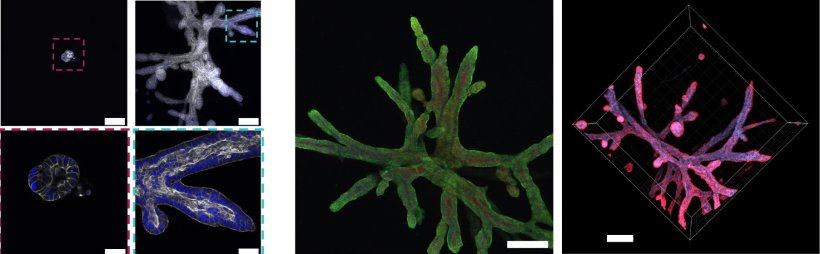
Image source: Randriamanantsoa et al., Nature Communications 2022 (CC BY 4.0)
For the formation of the organoid, the mechanical plasticity of the collagen – in other words, its ability to be reshaped – is an important factor. The forces exerted on the material through cell growth cause permanent deformation – unlike a purely elastic deformation, which would be reversible. “This organoid system enables us to track individual growth stages of the pancreatic cancer over time, such as cell divisions and movements, as well as gene expression patterns,” says Bausch. “Until now this was simply not possible because an accessible system was lacking.”
As a next step the researchers are already working on a tumor organoid grown from human pancreatic cancer cells. “On that basis, new treatments specifically designed for the various tumor progression phases can be identified and tested,” says Reichert. The goal is to identify treatments that fight specific subtypes of the pancreatic carcinoma and are thus more effective.
Source: Technical University of Munich
09.10.2022