News • HNSCC diagnostics
Head and neck cancer: Novel prognostic biomarker could double survival
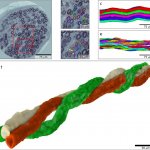
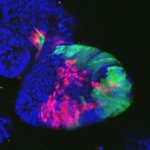
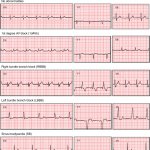
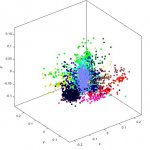
A recent study conducted by the Faculty of Medicine at The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CU Medicine) discovered a novel genetic biomarker which can predict the survival of head and neck cancer patients. There are over 0.7 million new head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) cases globally each year. However, currently there is no clinical implementation of any genetic biomarker to…