News • Increased risk of infection
Researchers identify cause for immunodeficiency after stroke and heart attack
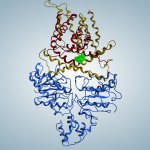
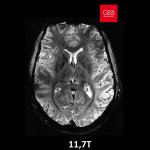
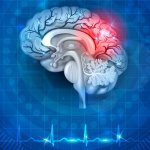
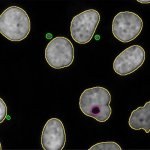
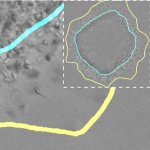
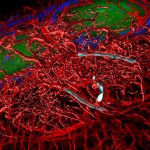
After a stroke or heart attack, the risk of infection is increased – however, why this happens was unknown. Now, researchers found a previously unknown cause – and a therapeutic approach.