News • Study explores regenerative potential
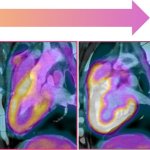
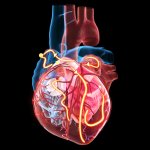
How the heart regrows muscle cells after a heart attack
Pioneering research has shown that heart muscle cells regrow after a heart attack, opening up the possibility of new regenerative treatments for cardiovascular disease.