News • Combining data science and machine learning
MRI image reconstruction: the next step for compressed sensing
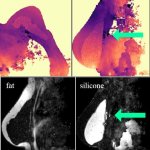
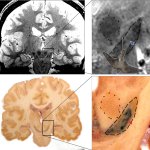
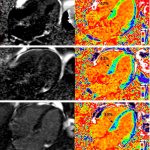
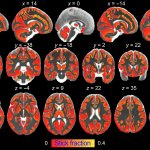
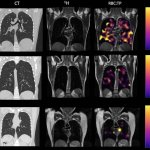
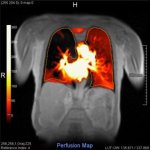
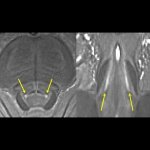
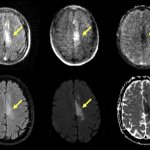
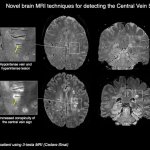
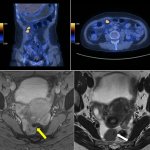
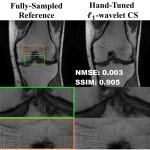
US scientists and engineers have found a way to improve the performance of traditional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) reconstruction techniques, allowing for faster MRIs to improve healthcare.