Photo: Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry
News • Easy-to-use
Free tool could reduce prostate cancer biopsies
A new risk calculator developed by a University of Alberta researcher and collaborators in the United States could reduce the number of unnecessary and invasive biopsies for prostate cancer.
Adam Kinnaird, a surgeon and assistant professor in the Faculty of Medicine & Dentistry, said the risk calculator is available online for free, requires only conventional clinical data paired with data from prostate MRI scans, and targets an unmet clinical need for prostate cancer patients.
More than one million prostate biopsies are performed in North America every year, and prostate cancer is the most common type of internal cancer in North American men. However, as Kinnaird explained, these biopsies aren’t always necessary and they come with certain risks.
“Only about 25 to 30 per cent of them may show some prostate cancer, and up to seven per cent of men, after they’ve had a prostate biopsy, end up getting hospitalized within 30 days. And, there’s a four per cent risk of what’s called post-biopsy sepsis, which can cause patients to end up in the ICU or may even prove fatal,” said Kinnaird, who is also a member of the Cancer Research Institute of Northern Alberta. “Anything we can do before the biopsy to determine whether the patient really needs a biopsy is very important for patient care.”
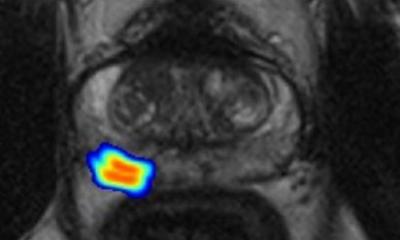
The risk calculator, called the PCRC-MRI, is the first in North America developed to predict biopsy outcomes in North American men. The combination of the standard-of-care data with MRI data provides two critical benefits: it triages patients to determine whether they truly need the biopsy in the first place, and if they do, it improves the technique so clinicians are better able to find more clinically significant prostate cancer.
To test the efficacy and accuracy of the calculator, Kinnaird led a study in which 2,354 men undergoing MRI-guided prostate biopsy were examined over 10 years. The results showed that the simple, free calculator significantly helped improve patient selection for biopsies.
“We did a net benefit analysis using this calculator. The analysis showed that we could safely avoid 16 biopsies out of every 100 at a risk threshold of 20 per cent. What that means is we could potentially be saving 16 men from having to undergo this invasive procedure that has serious potential side-effects,” said Kinnaird.
Kinnaird noted that the MRI-guided prostate biopsy is already a major improvement on the current standard of care in Alberta, called a 12-core transrectal ultrasound-guided biopsy.
“It’s basically a blind biopsy. An ultrasound probe can see the prostate, it can see the outline, but it cannot see if there’s actually any prostate cancer in the prostate,” Kinnaird explained. “So what’s done is the urologist or radiologist performing the biopsy takes 12 random samples from the prostate and hopes that they detect prostate cancer if it’s there.”
While many of the patients in the study received MRI-guided prostate biopsy at the University of California, Los Angeles, the U of A recently obtained a device called the UroNAV that allows patients here to receive the same type of biopsy and gives clinicians a new tool in their arsenal.
“It gives us something to aim at,” said Kinnaird. “We take what we’ve learned from the MRI being done on the patient and create a model of their prostate in the software. Then we can fuse it to the ultrasound being done in real time. It’s been shown to improve the detection of clinically significant prostate cancer and to reduce the rate or risk of identifying clinically insignificant prostate cancer, which is prostate cancer that we would not want to treat and therefore not want to detect.”
For the clinical data component, the PCRC-MRI examines certain variables that have previously been identified as risk factors for harbouring prostate cancer, from family history to an abnormal digital rectal examination.
The next steps involve creating more calculators that provide clinicians with beneficial information that can help with selecting patients for these invasive biopsies. Kinnaird is now working on a risk calculator for patients under active surveillance, which would examine the likelihood of their low-risk prostate cancer becoming more aggressive.
The research was published in the Canadian Urological Association Journal.
Quelle: University of Alberta
13.02.2022