News • Machine learning
Training a computer to classify breast cancer tumors
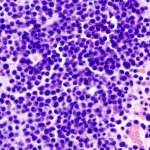
Using technology similar to the type that powers facial and speech recognition on a smartphone, researchers at the University of North Carolina Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center have trained a computer to analyze breast cancer images and then classify the tumors with high accuracy. In a study published in the journal NPJ Breast Cancer, researchers reported they used a form of artificial…