Article • Awareness, screening, therapies
Why Europe is in need of a new lung cancer strategy
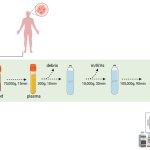
During a webinar, health experts and clinicians highlighted the need for urgent changes to lung cancer services across Europe to create a more cohesive and equal approach to care.