
Snake venom helps hydrogels stop the bleeding
A nanofiber hydrogel infused with snake venom may be the best material to stop bleeding quickly, according to Rice University scientists.

A nanofiber hydrogel infused with snake venom may be the best material to stop bleeding quickly, according to Rice University scientists.

Northwestern University scientists have developed the first liquid nanoscale laser. And it’s tunable in real time, meaning you can quickly and simply produce different colors, a unique and useful feature. The laser technology could lead to practical applications, such as a new form of a “lab on a chip” for medical diagnostics.
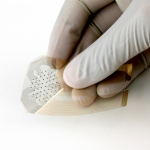
Engineers at the University of California, Berkeley, are developing a new type of bandage. Thanks to advances in flexible electronics, the researchers have created a new "smart bandage" that uses electrical currents to detect early tissue damage from pressure ulcers, or bedsores, before they can be seen by human eyes - and while recovery is still possible.

If you have diabetes, or cancer or even heart problems, maybe you should blame it on your dad’s behaviour or environment. Or even your grandfather’s. That’s because, in recent years, scientists have shown that, before his offspring are even conceived, a father’s life experiences involving food, drugs, exposure to toxic products and even stress can affect the development and health not…

Researchers from the University of Cologne and NEO New Oncology AG today jointly published in Nature* the findings of an extensive genomic analysis of neuroblastoma, a malignant pediatric tumor of the sympathetic nervous system. In the most aggressive forms of this tumor, the researchers identified previously unknown genomic alterations leading to up-regulation of the telomerase reverse…

A number of innovative research results were presented at the 24th Congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology that took place in Copenhagen from 7 to 11 October 2015. Some of these results are expected to impact medicine far beyond dermatology, demonstrating the innovative character of the specialty.
Scientists have evidence that Popeye was right: Spinach makes you stronger. But it’s the high nitrate content in the leafy greens — not the iron — that creates the effect.
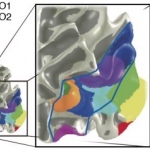
A study three years ago sparked a medical mystery when it revealed a part of the brain not found in any present-day anatomy textbooks. Recently, Indiana University computational neuroscientist Franco Pestilli and an international research team published an article in the journal Cerebral Cortex that suggests this missing part of the brain may play an important role in how we understand the world…

Juries in criminal cases typically decide if someone is guilty, then a judge determines a suitable level of punishment. New research confirms that these two separate assessments of guilt and punishment – though related - are calculated in different parts of the brain. In fact, researchers found that they can disrupt and change one decision without affecting the other.

University of Virginia School of Medicine researchers have discovered a new strategy for attacking cancer cells that could fundamentally alter the way doctors treat and prevent the deadly disease. By more selectively targeting cancer cells, this method offers a strategy to reduce the length of and physical toll associated with current treatments.
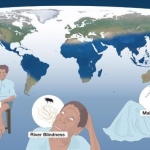
The Nobel Assembly at Karolinska Institutet has today decided to award the 2015 Nobel Prize in Medicine with one half jointly to William C. Campbell and Satoshi Ōmura for their discoveries concerning a novel therapy against infections caused by roundworm parasites and the other half to Youyou Tu for her discoveries concerning a novel therapy against Malaria.
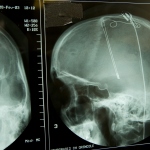
By implanting electrodes in the brain tissue one can stimulate or capture signals from different areas of the brain. These types of brain implants, or neuro-prostheses as they are sometimes called, are used to treat Parkinson's disease and other neurological diseases.
People often talk about how important it is to stay in shape, something humans usually can accomplish with exercise and a healthy diet, and other habits. But chances are, few of us ever think about the shape of our individual cells.

Researchers from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and Princeton University have designed a new online tool that predicts the role of key proteins and genes in diseases of the human immune system. Called “ImmuNet,” details of the publically available resource were published online in the journal Immunity.
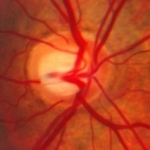
Scientists at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine have elucidated a genetic interaction that may prove key to the development and progression of glaucoma, a blinding neurodegenerative disease that affects tens of millions of people worldwide and is a leading cause of irreversible blindness.

More than five million Americans are living with Alzheimer's disease (AD). Of them, 400,000 also have Down syndrome. Both groups have similar looking brains with higher levels of the protein beta amyloid.
A gap in scientific knowledge about a family of drugs that are used to treat Type 2 diabetes has been highlighted in a new study.

MRSA is bad news. If you've never heard of it, here's what you need to know: It's pronounced MER-suh, it's a nasty bacterial infection and it can cause serious disease and death. Senior molecular biology major Jacob Hatch knows MRSA as the infection that took his dad's leg.
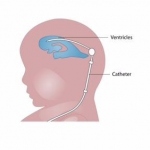
Fetuses with enlarged ventricles--the fluid-filled cavities inside the brain--may be less likely than their counterparts to benefit from surgery in the womb to treat spina bifida, according to a study supported by the National Institutes of Health.
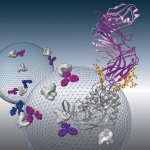
Proteins called broadly neutralizing antibodies (bNAbs) are a promising key to the prevention of infection by HIV, the virus that causes AIDS, say researchers at California Institute of Technology.

‘In IT we often casually say that Big Data is exactly what we can’t do yet,’ said Professor Christoph Meinel, President of Germany’s Hasso-Plattner-Institute, ruefully. We asked the computer science expert about the potential of big data in medicine and medical research.

For patients with an often-deadly form of leukemia, new research suggests that lingering cancer-related mutations – detected after initial treatment with chemotherapy – are associated with an increased risk of relapse and poor survival.

Scientists at Karolinska Institutet and Karolinska University Hospital in Sweden have discovered a new explanation for severe early infant epilepsy. Mutations in the gene encoding the protein KCC2 can cause the disease, hereby confirming an earlier theory. The findings are being published in the journal Nature Communications.

Researchers at the University of Alberta have found that spinal manipulation--applying force to move joints to treat pain, a technique most often used by chiropractors and physical therapists--does indeed have immediate benefits for some patients with low-back pain but does not work for others with low-back pain.
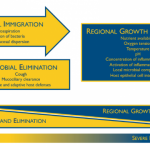
With every breath you take, microbes have a chance of making it into your lungs. But what happens when they get there? And why do dangerous lung infections like pneumonia happen in some people, but not others? Researchers at the University of Michigan Medical School have started to answer these questions by studying the microbiome of the lungs – the community of microscopic organisms that are…