
News • New printing method
Self-folding 4D electrodes enhance nerve stimulation
Using 4D printing technology, researchers have developed flexible electrodes. On contact with moisture, they automatically fold and wrap themselves around thin nerves.

Using 4D printing technology, researchers have developed flexible electrodes. On contact with moisture, they automatically fold and wrap themselves around thin nerves.

A placenta on a chip developed at the University of Dundee has the potential to transform research into life-threatening conditions in pregnancy.

The consortium Holland Hybrid Heart will receive €10 million to develop a soft robotic heart suitable for transplantation.

By using genetic data on multiple traits from people of non-European ancestry, scientists have improved the accuracy of polygenic scores in predicting disease risk for all.
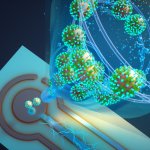
Combining aerosol sampling and ultrasensitive biosensing, researchers have created a real-time monitor that can detect any of the Sars-CoV-2 virus variants in a room in about 5 minutes.

Do coronavirus vaccines skew the menstrual cycle, cause more bleeding or pain? Anecdotal reports hint at a connection. Now, a new study led by Boston University provides answers.
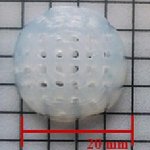
Researchers from Queen’s University Belfast have created personalised 4D printed “smart” implants for breast cancer management - a first for this technology.

Ongoing research at the University of Roehampton, UK has identified the upper critical temperature (UCT) for humans - and why our bodies cannot handle more heat.

Research by the University of Southampton has shown that repeated Covid-19 vaccination increases the ability of lymphoma patients to prevent infection from the virus, particularly after four doses.

Missing crucial doses of medicines and vaccines could become a thing of the past thanks to Rice University bioengineers’ technology for making time-released drugs.

The old adage that expectant mums are ‘eating for two’ and don’t need to worry about weight gain can lead to health consequences for mum and baby, maternal health experts warn.

A new publication discusses deep-ultraviolet (DUV) photonics for the disinfection of Sars-CoV-2 and its variants (Delta and Omicron) in the cryogenic environment.

A new US-led study shows that astrocyte brain cells play an important role in promoting brain metastasis by recruiting a specific subpopulation of immune cells.

For proton radiation therapy against cancer, there is yet no direct method for mapping the beam range during dose delivery. A new method devised by Dresden scientists could help.

German scientists have developed a magnetically controlled soft medical robot with a unique, flexible structure inspired by the body of a pangolin, that could heat up to mitigate bleeding.
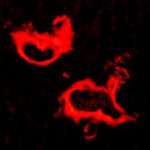
A research team from Barcelona studied the liver of Alzheimer's disease mice models, and demonstrated the importance of the liver-brain axis regarding the psychological symptoms of the disease.

A gel that combines both stiffness and toughness is a step forward in the bid to create biodegradable implants for joint injuries, according to new research from the University of British Columbia.
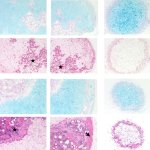
A Japanese research group has developed a method using iPS cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells (iMSC) to create cartilage spheroids, offering new possibilities for tissue repair.

Gentle cleansers are just as effective in killing viruses – including coronavirus – as harsh soaps, according to a new study from scientists at the University of Sheffield.

To ensure that wounds remain tightly sealed in the abdomen after surgery, researchers at Empa and ETH Zurich have developed a patch with a sensor function.

US researchers identified a potential breakthrough in glioblastoma treatment. Using a modified virus, they created a treatment that specifically attacks tumor cells, while leaving normal cells intact.

Women suffering from multiple sclerosis temporarily get much better when pregnant. Researchers have now identified the beneficial changes naturally occurring during pregnancy.
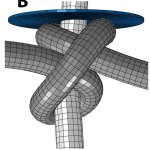
Knots are a crucial part of surgery, but surprisingly little is known about how they work. To fill this gap, a team at EPFL started the first physics-based study on the mechanics of surgical knots, and exactly what properties influence their strength.
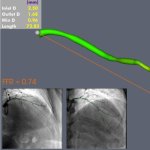
Patients with heart disease could benefit from less extensive interventions thanks to technology that creates 3D computer models of blood flow through the heart's arteries, according to new research.

A new method for cheaply producing heart valves in the span of minutes shows great promise. The scientists describe the method as "a cotton-candy machine with a hair dryer behind it."