News • Microbial influence on treatment
Study explores the role of bacteria in cancer
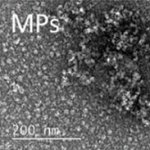
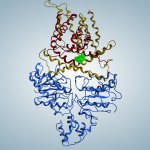
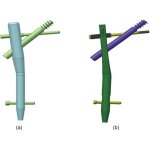
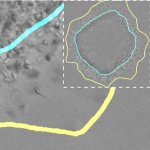
Bacteria can help – or hinder – the treatment of cancer. How this happens, however, is largely unknown. Now, researchers have mapped bacteria in cancer metastases to shed more light on their role.