News • Vortex fluidic device
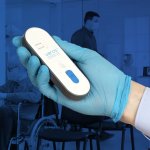
Next step in rapid diagnostics for infectious diseases
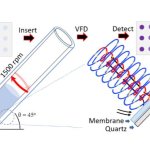
The speedy, high-tech method of inexpensive, accurate and high-throughput protein biomarker assay testing is being touted as a much-needed development in point-of-care (PoC) testing.