Lab-on-a-chip
Multiplexed lab-on-a-chip bioassays for testing antibodies against SARS-CoV 2 and its variants in multiple individuals
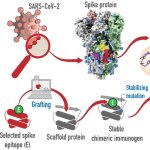
The coronavirus pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2 and its variants is still a major public safety issue worldwide. The “alpha” variant B.1.1.7, the “gamma” variant P.1, the “beta” variant B.1.351, and the “delta” variant B.1.617 are of particular concern because of their high prevalence. Large-scale vaccination and sensitive detection are vital for preventing the spread of Covid-19.