News • Device for precise neuromodulation
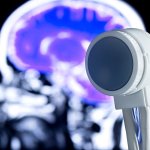
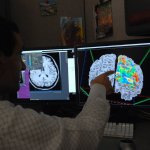
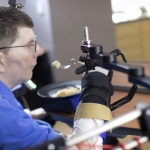
Ultrasound helmet enables deep brain stimulation without surgery
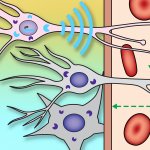
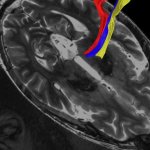
A new ultrasound helmet capable of influencing deep brain regions without surgery opens up new possibilities for neurological research and treatment of disorders such as Parkinson’s disease.