News • Promising treatment target
"Partner-in-crime" of colorectal cancer discovered
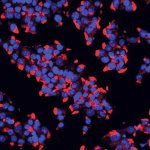
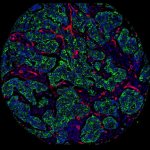
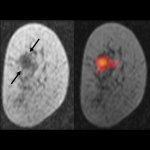
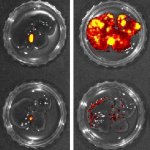
A protein that helps colorectal cancer cells spread to other parts of the body could be an effective treatment target, researchers from Hokkaido University discovered. Colorectal cancer patients with an immune system-regulating protein called interleukin 6 (IL-6) are more likely to have recurring tumors that can also spread to the liver, according to research published in the journal Cancer…