News • ER-positive tumour BC
Drug target for aggressive breast cancer found
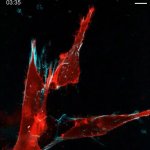
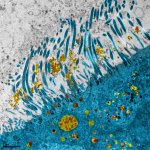
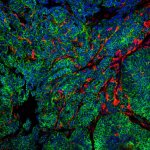
A team of British and American scientists have discovered a way to slow the growth of breast cancer stem cells in the lab. The study led by Dr Bruno Simões and Professor Rob Clarke from The University of Manchester could eventually lead to combination drug therapies on previously untreatable breast cancers. Around three quarters of women who have breast cancer have what are known as oestrogen…